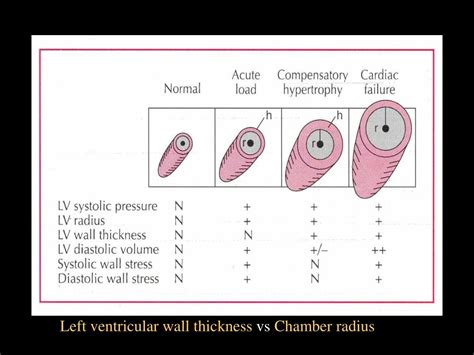
when you measure thickness of ventricular walls|mildly increased septal wall thickness : dealers Normal sex- and age-specific reference ranges for left ventricular mid-diastolic wall thickness (LV-MDWT) at prospective electrocardiographically triggered mid-diastolic CT angiography were provided, and LV-MDWT was . Compre Topo de Bolo Cachaceira no Elo7 por R$ 24,60 | Encontre mais produtos de Topo de Bolo de Aniversário e Aniversário e Festas parcelando em até 12 vezes | Topo de Bolo Cachaceiro - Ao efetuar a .
{plog:ftitle_list}
webVocê está aqui: Página Principal > Serviços > Consultar CT-e. Consultar CT-e
How to Measure Wall Thickness with Echocardiography - YouTube. ASE360. 31K subscribers. Subscribed. 619. From an accredited US healthcare educator. Learn how experts define health sources in.
Relative Wall Thickness helps calculate if the ventricular morphology has altered. The RWT reports the relationship between the wall thickness and cavity size. The RWT is calculated by doubling the dimension of .
normal ventricular wall thickness
normal left ventricle wall thickness
3 External links. The Left Ventricle. Example: Measurement end - Diastolic wall thickness (red) + LV diameter (green) Each echocardiogram includes an evaluation of the LV dimensions, wall thicknesses and function. . Normal sex- and age-specific reference ranges for left ventricular mid-diastolic wall thickness (LV-MDWT) at prospective electrocardiographically triggered mid-diastolic CT angiography were provided, and LV-MDWT was . Left ventricular mass, wall thickness, and the ratio of wall thickness to radius are important measures to characterize the spectrum of left ventricular geometry. For clinicians, an increase in left ventricular mass is the hallmark of .The mitral valve allows blood to flow from the left atrium into left ventricle, tricuspid stops back flow of blood. Semilunar valves permit blood to be forced into arteries. Compare and contrast .
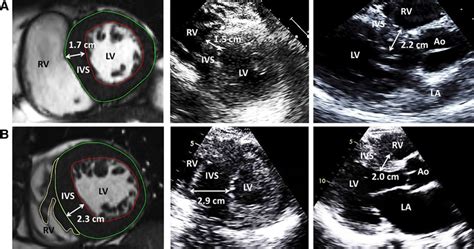
We sought to compare maximal left ventricular (LV) wall thickness (WT) measurements as obtained by routine clinical practice between echocardiography and cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) and document .Figure 7 – IVS tool - measuring the thickness of the intraventricular septum (IVS) and left ventricular posterior wall (LVPW) as well as the left ventricular internal diameter (LVID). These .Specifically, LV EDD and ESD measurements are obtained by drawing a line measuring the distance between the anteroseptal and inferolateral walls (Fig.A-D). In addition, linear measures of wall thickness are routinely made to . Purpose To generate normal reference values for left ventricular mid-diastolic wall thickness (LV-MDWT) measured by using CT angiography. Materials and Methods LV-MDWT was measured in 2383 consecutive .
Right Ventricle 692 RV Wall Thickness 692 RV Linear Dimensions 693 C. RVOT 694 Fractional Area Change and Volumetric Assessment of the Right Ventricle 696 . to be performed and reported should include a measure of right ventricular (RV) size, right atrial (RA) size, RV sys- Echocardiographic measurements of minor axis and wall thickness and calculations from these two measurements of left ventricular end-diastolic volume and mass were performed in 24 patients and compared with angiocardiographic measurements of the same variables in corresponding patients. The echo-measured left ventricular end-diastolic . Diagnosis of HCM relies on echocardiogram and cardiac MRI showing hypertrophied left ventricle (LV) without dilatation in the absence of other metabolic or systemic disease causing hypertrophy such as hypertension or valvular disease. In adults, diagnosis of HCM is based on a maximum LV thickness of ≥15 mm at any site.
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is a condition in which there is an increase in left ventricular mass, either due to an increase in wall thickness or due to left ventricular cavity enlargement, or both. Most commonly, the left ventricular wall thickening occurs in response to pressure overload, and chamber dilatation occurs in response to the volume overload.[1]Right Ventricular Hypertrophy: If the heart adapts to become too thick, it will not be able to pump blood as efficiently, and heart failure may occur. 17.1F: Myocardial Thickness and Function is shared under a CC BY-SA license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. Background—We sought to compare maximal left ventricular (LV) wall thickness (WT) measurements as obtained by routine clinical practice between echocardiography and cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) and document causes of discrepancy. Methods and Results—One-hundred and ninety-five patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (median .
Question: When you measured thickness of ventricular walls, was the right or left ventricle thicker?Knowing that structure and function are related, how would you say this structural difference reflects the relative functions13. Semilunar valves prevent backflow into the mitral and tricuspid valves prevent backflow intothe Using your own . Introduction. Left ventricular mass (LVM) is a well-established measure that can independently predict adverse cardiovascular events and premature death. 1-3 Population-based studies have revealed that increased LVM and left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) as assessed by two-dimensional (2D) M-mode echocardiography measurements provide prognostic .Ventricular contraction ejects blood into the major arteries, resulting in flow from regions of higher pressure to regions of lower pressure. . resistance and pressure, but decreasing flow. Venoconstriction, on the other hand, has a very different outcome. The walls of veins are thin but irregular; thus, when the smooth muscle in those walls . Cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) can accurately measure left ventricular (LV) mass, and several measures related to LV wall thickness exist. We hypothesized that prognosis can be used to .
mildly increased septal wall thickness
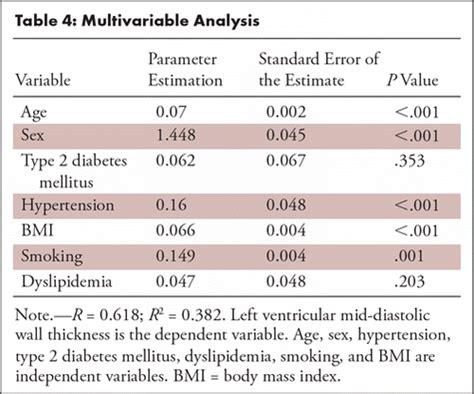
Background—Increased left ventricular myocardial thickness (LVMT) is a feature of several cardiac diseases. The purpose of this study was to establish standard reference values of normal LVMT with cardiac magnetic resonance and to assess variation with image acquisition plane, demographics, and left ventricular function. Methods and Results—End . Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is characterized by left ventricular hypertrophy (wall thickness >12-15 mm; normal wall thickness is 12 mm or less, measured during diastole) without obvious etiology. Associated right ventricular hypertrophy may .The most widely used approach to judging hypertrophy is to measure the thickness of the left ventricular walls. 1 Increased left ventricular wall thickness is then used as a guide for further diagnostic and invasive evaluation. This is a report of two patients with proven hemodynamically critical aortic stenosis who, nevertheless, had normal .Let’s now review 6 pitfalls to avoid when measuring the left ventricular wall and chambers. Avoid RV Trabeculations. Be careful when measuring the IVS in the presence of right ventricular trabeculations . In my lab we measure both a .
When you measured thickness of ventricular walls, was the right or left ventricle thicker? . Knowing that structure and function are related, how would you say this structural difference reflects the relative functionsLeft ventricular hypertrophy affects an estimated 15% to 20% of the population — nearly 1 in 5 people. You may have an increased risk of LVH if you have high blood pressure or have obesity, are elderly or Black. How serious is left ventricular hypertrophy? Left ventricular hypertrophy usually occurs as a result of other heart problems.
Left ventricular hypertrophy is thickening of the walls of the lower left heart chamber. The lower left heart chamber is called the left ventricle. The left ventricle is the heart's main pumping chamber. During left ventricular hypertrophy, the thickened heart wall can become stiff. Blood pressure in the heart increases.
Question: What was the measured thickness of the left ventricle wall? _____ What was the measured thickness of the right ventricle wall? _____ Show transcribed image text. There are 2 steps to solve this one. Solution. Step 1. In a healthy individual,. View the full answer. Step 2. Unlock. Answer. Low pressure is sufficient because blood is forced only a short distance; from the left atrium down to the left ventricle. The muscular walls of the left ventricle are much thicker and generate much higher pressure, as shown on the graph. . Measuring Enzyme Activity; 1.4.5 Maths Skill: Drawing a Graph for Enzyme Rate Experiments; 1.4.6 Maths . Also, as a subpulmonary ventricle, the RV has a lower ejection fraction and thinner walls than the left ventricle. RV wall thickness is usually 3 to 5 mm, the proportion between right ventricle and left ventricle being as 1 to 3 ; it is thickest at the base and gradually becomes thinner toward the apex. Purpose To compare transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) and cardiac MRI measurements of left ventricular mass (LVM) and maximum wall thickness (MWT) in patients with Fabry disease and evaluate the clinical significance of discrepancies between modalities. Materials and Methods Seventy-eight patients with Fabry disease (mean age, 46 years ± 14 .
We measure the external diameter of the left ventricle of a heart. Enter your patient's interventricular septal end-diastole measurement (IVSd) It is also measured with echo. We evaluate the thickness of the wall that is located between the two ventricles of a heart. Enter your patient's posterior wall thickness at end-diastole (PWd) Measured .ated, and thus, the traditional assessment of left ventricular (LV) end-diastolic volume, LV end-diastolic wall thickness, and LV ejection fraction (EF) as performed with echocar-diography and cardiac MRI (5) cannot be performed. Quantification of LV EF, LV mass, and LV wall thickness provides diagnostic and prognostic informa-tion (6,7). An enlarged or thickened heart — a condition doctors call left-ventricular . “We use echocardiography to measure the septum that divides the two ventricles, as well as the back wall of the .
448 Review Sheet 30 you measured thickness of ventricular walls, was the right or left ventricle thicker? are related, how would you say this structural difference reflects the relative functions of these two heart chambers? 13. Semilunar valves prevent backflow into the mitral and tricuspid valves prevent backflow into the Using your own .
lv wall thickness normal values
Introduction. An accurate and reproducible quantification of the left ventricular (LV) structure is important for diagnosis and monitoring of disease progression, for timing of intervention and for discrimination of prognosis. 1–3 LV chamber size and wall thickness represent the determinants of decision-making in several clinical guidelines. 1, 4, 5 .
left ventricular wall thickness chart
left ventricle wall thickness guidelines
increased ventricular wall thickness
26 de dez. de 2023 · O selo de segurança ou cadeado verde por si só não garante que um site é confiável, mas é requisito mínimo para os dias de hoje. Verifique todas as .
when you measure thickness of ventricular walls|mildly increased septal wall thickness